PROF. DR. MED. KLAUS WENKE
Specialist for Cardiac Surgery
- Specialist for cardiac surgery, sports medicine, cardiosurgical intensive medicine, thorax and cardiovascular surgery
- Member of the Medical Board Bavaria
- Medical licence acquired in the Federal Rebublic of Germany
- Member of the Association of Statutory Health Insurance Physicians Bavaria: KV Nr. 64/07072
Career
- Medical studies at the universities of Münster, Göttingen, Heidelberg, Würzburg and the University of Bern, Switzerland
- The residency in general surgery at the Klinikum Memmingen was followed by a commission as research assistant at the cardiosurgical clinic and polyclinic of the Klinikum Großhadern of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munich. Headed by Prof. Dr. W. Klinner and Prof. Dr. B. Reichart
- After acquisition of the designation thorax and cardiovascular surgery Klaus Wenke habilitated in the discipline cardiac surgery and serves as university lecturer of the medical faculty of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität in Munich.
- Most recently senior physician at the cardiosurgical clinic at München-Bogenhausen
Memberships
- Member of the German Society of Cardiology, Heart and Circulation Research
- Member of the German Society of Cardiac, Thorax and Vascular Surgery
- Member of the Bavarian Society of Sports Medicine
Cardiac Surgery
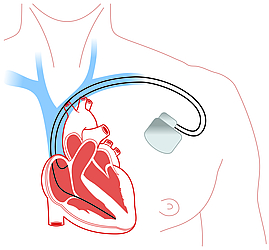
Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers
The treatment of slow cardiac arrythmia in many cases includes the implantation of a cardiac pacemaker. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia in an operating room or a cardiac catheter laboratory of a clinic. The aggregate of the cardiac pacemaker is usually placed in the area of the right upper chest directly under the skin. From there the probes of the device can be washed into the right ventricle and be embedded there. With the help of the probes the heart can be regularly stimulated in order to normalize its rhythm.
Implantation of Defibrillators
In some cases patients with life-theatening fast cardiac arrythmias need the implantation of a defibrillator in order to avoid sudden cardiac death. The systems are able to detect ventricular fibrillation and to regularize the cardiac rhythm by discharging short electrical impulses. This procedure greatly improves the survival rate of affected patients. The operation very much resembles the implantation of a cardiac pacemaker, only the aggregate is more voluminous due to a stronger battery.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT implantation)
Alongside a medicinal therapy some patients suffering from chronic cardiac insufficency can be helped with a resynchronization therapy. The special cardiac pacemaker system (biventricular cardiac pacemaker, CRT system) used in this case is able to stimulate the right ventricle as well as the left one. The operation very much resembles the conventional implantation of a cardiac pacemaker. However an additional third probe is embedded in a cardiac vein at the left ventricle. Furthermore the aggregate is more voluminous than a conventional cardiac pacemaker due to a necessary stronger battery. If needed devices of this kind can be additionally fitted with a defibrillator function.
Bypass Surgery
In Western society coronary heart disease is the most common condition of the cardiovascular system. Lack of exercise, hypertension, dyslipidemia, nicotine consumption and negative stress are the main reasons for the calcification or obstruction of coronary vessels (coronary arteries). The inadequate blood supply generates an oxygen deficiency within the myocardium with a corresponding pain symptomatology, in other words: a heart attack.
A reliable therapy for this condition offers the coronory bypass surgery. With 70 % this procedure represents the most common cardiosurgical operation among adults. The operation is performed classically with the help of a heart-lung machine as well as minimally invasive on the beating heart. These days chest wall arteries, forearm arteries and superficial leg veins are used to create bypass vessels. The procedure normally takes 3 to 4 hours, the average residence time at the hospital amounts up to 10 - 12 days. Thereafter a 3 week rehabilitation takes place.
Aortic Valve Replacement
Aortic valve replacement represents the most common heart valve procedure. These days it is performed even well into advanced age since aortic valve conditions become more frequent within this age group. The classic operation requires the opening of the chest cavitiy to replace the malfunctioning heart valve with an artificial one. The surgery time takes up to 3-4 hours. Mechanical and biological valve protheses are used in accordance with the age of the patient. After the operation the implantation of a mechanical heart valve requires a permanent hemodilution (for example with Marcumar).
Mitral Valve Reconstruction
The second leading cardiac valve operation is the reconstruction of the mitral valve. As a general rule leakage on this cardiac valve is remedied via surgical correction of the valve leaflets. The valve leaflets are reconstructed with the help of artificial sinews or by removal of defect valve parts. An artificial ring around the valve (mitral ring) stabilizes the reconstructive result. The surgery time can take up to 4 hours. These days appoximately 90% of all mitral valve deficiencies can be repaired like this. A permanent hemodilution (for example with Marcumar) after an operation of this kind is not necessary. Only very few cases require the complete replacement of the mitral valve with a biological or mechanical prothesis. The tricuspid valve offers a further option for a reconstructive procedure.










